
ICD-10-CM Coding for Hemorrhoids Simplified – Medical Coding Buff Expand Search Toggle Menu Search Previous Continue Search Expand Toggle Menu Close Search
Learn the different types of hemorrhoids, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, and ICD-10-CM coding for hemorrhoids. Coding examples are provided. Medical Coding Buff

ICD-10-CM Coding for Hemorrhoids Simplified – Medical Coding Buff Expand Search Toggle Menu Search Previous Continue Search Expand Toggle Menu Close Search
Learn the different types of hemorrhoids, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, and ICD-10-CM coding for hemorrhoids. Coding examples are provided. Medical Coding Buff

ICD-10-CM Coding for Hemorrhoids Simplified – Medical Coding Buff Expand Search Toggle Menu Search Previous Continue Search Expand Toggle Menu Close Search
Learn the different types of hemorrhoids, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, and ICD-10-CM coding for hemorrhoids. Coding examples are provided. Medical Coding Buff
AMA Confirms Proper Coding for Ultroid Hemorrhoid Treatment – AAPC Knowledge Center
Until recently, providers using Ultroid® didn’t have a clear code choice to report Ultroid® treatment as a nonsurgical method to treat hemorrhoids.

ICD-10-CM Coding for Hemorrhoids Simplified – Medical Coding Buff Expand Search Toggle Menu Search Previous Continue Search Expand Toggle Menu Close Search
Learn the different types of hemorrhoids, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, and ICD-10-CM coding for hemorrhoids. Coding examples are provided. Medical Coding Buff

ICD-10-CM Coding for Hemorrhoids Simplified – Medical Coding Buff Expand Search Toggle Menu Search Previous Continue Search Expand Toggle Menu Close Search
Learn the different types of hemorrhoids, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, and ICD-10-CM coding for hemorrhoids. Coding examples are provided. Medical Coding Buff
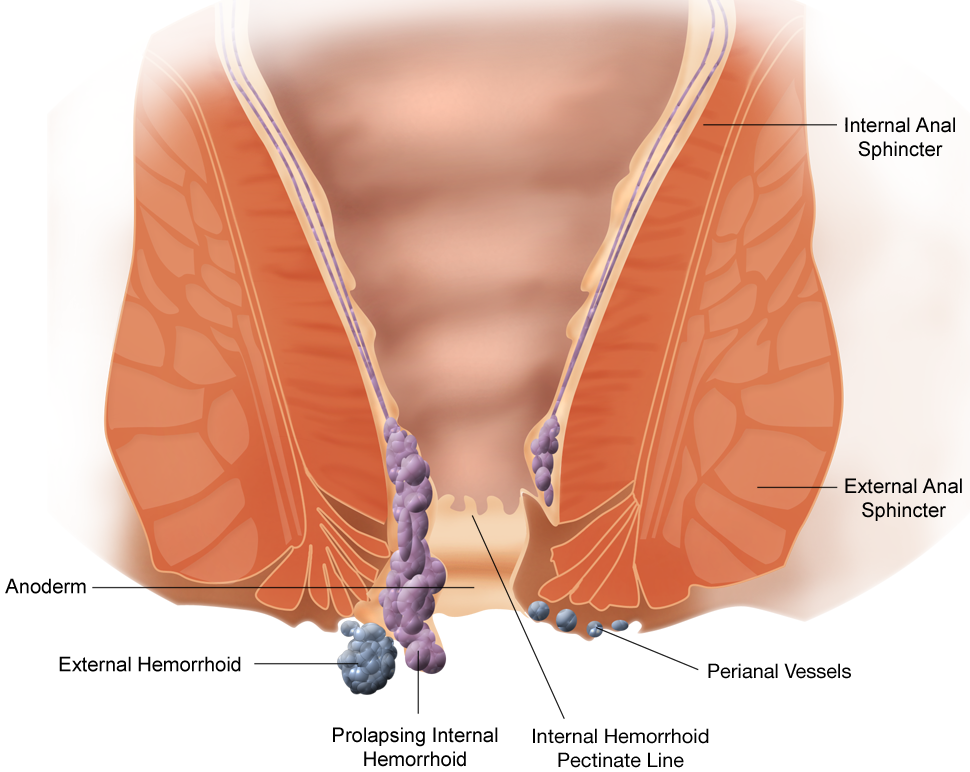
File:Hemorrhoid.png – Wikimedia Commons

Hemorrhoids Or Cancer – How To Spot The Difference
Hemorrhoids and cancer have some overlapping symptoms, which can make it difficult to determine if hemorrhoids or cancer is at the root of your issue.
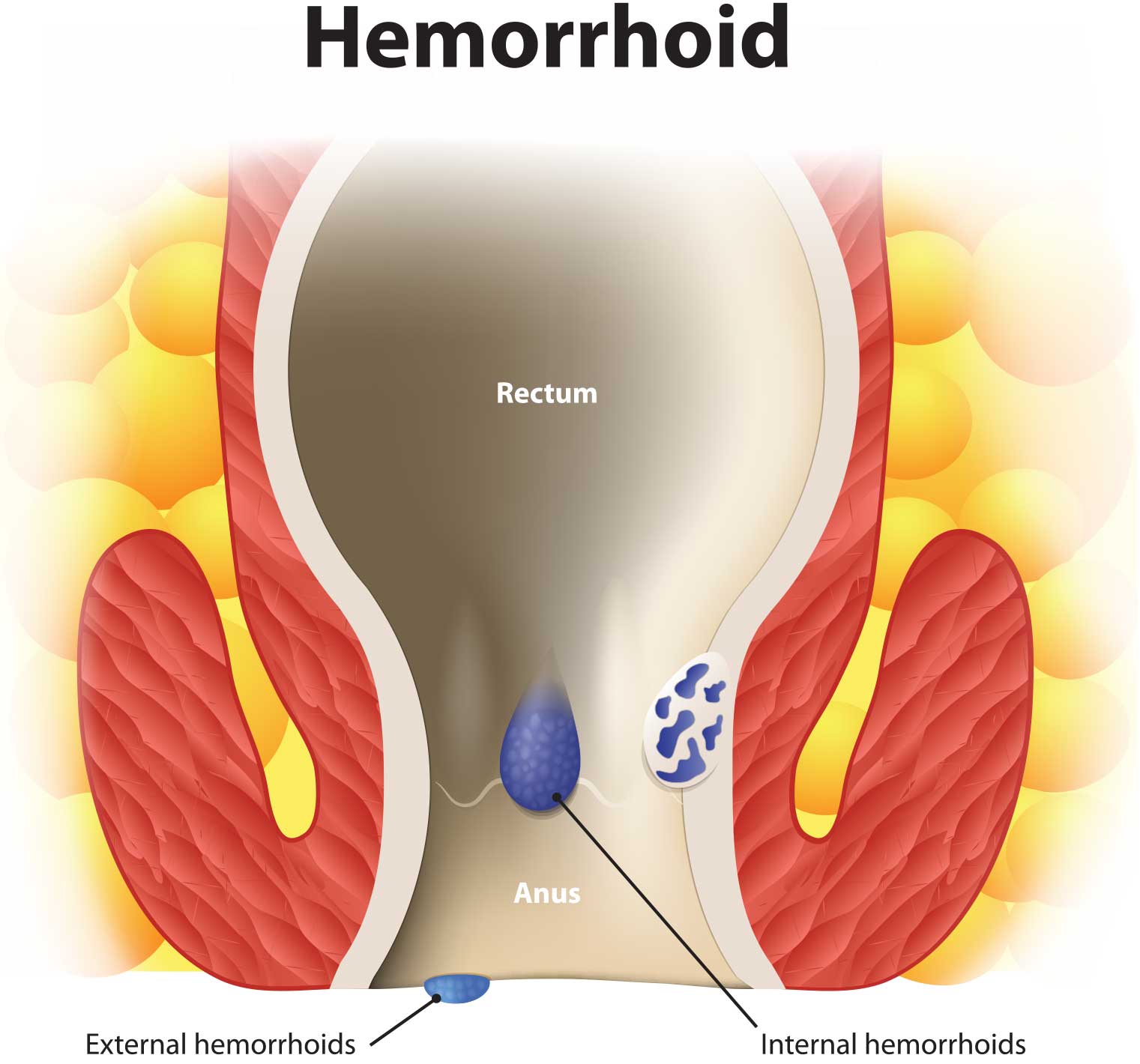
Hemorrhoids

Hemorrhoidectomy CPT code – simplify medical coding – YouTube
Simplify Medical coding Institute. Online Courses offered. Basic and Advanced Medical coding. CPC Exam training. Whatsapp: +91 9360951544.simplify medical…

Stapled hemorrhoidopexy – Wikipedia

Hemorrhoids Or Cancer – How To Spot The Difference
Hemorrhoids and cancer have some overlapping symptoms, which can make it difficult to determine if hemorrhoids or cancer is at the root of your issue.

Hemorrhoid – Wikipedia

List of drugs/medicine used for Hemorrhoids (Piles)
View list of generic and brand names of drugs used for treatment of Hemorrhoids(Piles ). Find more information including dose, side effects of the Hemorrhoids(Piles ).
ICD-10 Version:2010
ICD-10 Online contains the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision)
Digestive Health Associates
Review of frequently asked questions relating to colonoscopy
Hemorrhoid self removal
What Happens When You Squeeze or Pop ItWe include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process. Can you pop a…
Hemorrhoids – Online Dermatology
Hemorrhoids are a normal part of the rectal area and is very common but harmless. They are the veins that encompass the mucus membranes in this region

Hemorrhoids – Online Dermatology
Hemorrhoids are a normal part of the rectal area and is very common but harmless. They are the veins that encompass the mucus membranes in this region

Development of the ICD-10 simplified version and field test | Semantic Scholar Semantic Scholar
The field trial results demonstrated that the APN I CD-10 simplified version is feasible for implementation as an effective tool to implement ICD-10 clinical coding for hospitals, and developing countries may consider adopting the APn ICD/APN simplified version for Icd-10 code assignment in hospitals and health care centres. Background: The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10) has been used in various Asia-Pacific countries for more than 20 years. Although ICD-10 is a powerful tool, clinical coding processes are complex; therefore, many developing countries have not been able to implement ICD-10-based health statistics (WHO-FIC APN, 2007). Objective: This study aimed to simplify ICD-10 clinical coding processes, to modify index terms to facilitate computer searching and to provide a simplified version of ICD-10 for use in developing countries. Method: The World Health Organization Family of International Classifications Asia-Pacific Network (APN) developed a simplified version of the ICD-10 and conducted field testing in Cambodia during February and March 2016. Ten hospitals were selected to participate. Each hospital sent a team to join a training workshop before using the ICD-10 simplified version to code 100 cases. All hospitals subsequently sent their coded records to the researchers. Results: Overall, there were 1038 coded records with a total of 1099 ICD clinical codes assigned. The average accuracy rate was calculated as 80.71% (66.67–93.41%). Three types of clinical coding errors were found. These related to errors relating to the coder (14.56%), those resulting from the physician documentation (1.27%) and those considered system errors (3.46%). Discussion: The field trial results demonstrated that the APN ICD-10 simplified version is feasible for implementation as an effective tool to implement ICD-10 clinical coding for hospitals. Conclusion: Developing countries may consider adopting the APN ICD-10 simplified version for ICD-10 code assignment in hospitals and health care centres. The simplified version can be viewed as an introductory tool which leads to the implementation of the full ICD-10 and may support subsequent ICD-11 adoption.

Round Table 142: Navigating ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Coding Hot Spots – Ciox
Coding Hot Spots Its accessible through a link that will provide in our follow-up e-mail, we sent out this afternoon.
Diagnosa Icd 10 New | PDF
Scribd is the worlds largest social reading and publishing site.
Digestive Health Associates
Review of frequently asked questions relating to colonoscopy

Kode icd 10 hemorrhoid external, Interna, Grade 1, 2, 3, dan 4 – INOVASITEKNO.COM
Kode icd 10 hemorrhoid external, Interna, Grade 1, 2, 3, dan 4 – Hemoroid adalah penyakit yang ditandai dengan pembesaran pembuluh darah di daerah anus.

Piles in Pregnancy – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Health Tips
Hemorrhoids / Piles during pregnancy in younger women are not uncommon and can cause itching, discomfort and sometimes bleeding during bowel movement.

IJERPH | Free Full-Text | Colorectal Cancer Risk in Patients with Hemorrhoids: A 10-Year Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common disease and one of the leading causes of cancer deaths worldwide. This retrospective cohort study evaluated the risk of developing CRC in people with hemorrhoids. Using Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database, we established three sets of retrospective study cohorts with and without hemorrhoids. The first set of cohorts were matched by sex and age, the second set of cohorts were matched by propensity score without including colonoscopies, and the third set of cohorts were matched by propensity score with colonoscopies, colorectal adenomas, and appendectomies included. In the second set of cohorts, 36,864 persons with hemorrhoids that were diagnosed from 2000 to 2010 and a comparison cohort, with the same size and matched by propensity score, were established and followed up to the end of 2011 to assess the incidence and Cox proportional regression-measured hazard ratio (HR) of CRC. The overall incidence rate of CRC was 2.39 times greater in the hemorrhoid cohort than it was in the comparison cohort (1.29 vs. 0.54 per 1000 person-years), with a multivariable model measured adjusted HR of 2.18 (95% CI = 1.78–2.67) after controlling for sex, age, and comorbidity. Further analysis on the CRC incidence rates among colorectal sites revealed higher incidence rates at the rectum and sigmoid than at other sites, with adjusted HRs 2.20 (95% CI = 1.48–3.28) and 1.79 (95% CI = 1.06–3.02), respectively. The overall incidence rates of both cohorts were similar in the first and second sets of cohorts, whereas the rate was lower in the third set of hemorrhoid cohorts than in the respective comparison cohorts, probably because of overmatching. Our findings suggest that patients with hemorrhoids were at an elevated risk of developing CRC. Colonoscopy may be strongly suggested for identifying CRC among those with hemorrhoids, especially if they have received a positive fecal occult blood test result.
ICD-10 Education Session – ppt download
Agenda Topic Timeframe Presenter/s Welcome 15 minutes Anupam Goel, MD Documenting for ICD minutes Thomas Kravis, MD Clinical Informatics/Clinical Documentation Improvement (CD)/Coding- How can we help you? 30 minutes Cheryl Hager Stephen Crouch, MD & Kelly Tarpey Lou Ann Schraffenberger & Dawn Monegato Break Using CareConnection to Improve Documentation Case Examples Discussion 45 minutes
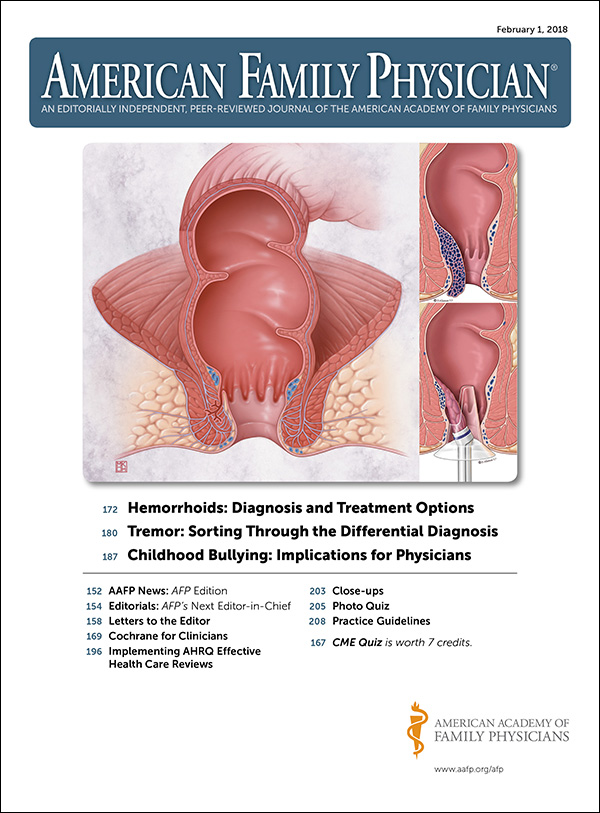
Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis and Treatment Options | AAFP
Many Americans between 45 and 65 years of age experience hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidal size, thrombosis, and location (i.e., proximal or distal to the dentate line) determine the extent of pain or discomfort. The history and physical examination must assess for risk factors and clinical signs indicating more concerning disease processes. Internal hemorrhoids are traditionally graded from I to IV based on the extent of prolapse. Other factors such as degree of discomfort, bleeding, comorbidities, and patient preference should help determine the order in which treatments are pursued. Medical management (e.g., stool softeners, topical over-the-counter preparations, topical nitroglycerine), dietary modifications (e.g., increased fiber and water intake), and behavioral therapies (sitz baths) are the mainstays of initial therapy. If these are unsuccessful, office-based treatment of grades I to III internal hemorrhoids with rubber band ligation is the preferred next step because it has a lower failure rate than infrared photocoagulation. Open or closed (conventional) excisional hemorrhoidectomy leads to greater surgical success rates but also incurs more pain and a prolonged recovery than office-based procedures; therefore, hemorrhoidectomy should be reserved for recurrent or higher-grade disease. Closed hemorrhoidectomy with diathermic or ultrasonic cutting devices may decrease bleeding and pain. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy elevates grade III or IV hemorrhoids to their normal anatomic position by removing a band of proximal mucosal tissue; however, this procedure has several potential postoperative complications. Hemorrhoidal artery ligation may be useful in grade II or III hemorrhoids because patients may experience less pain and recover more quickly. Excision of thrombosed external hemorrhoids can greatly reduce pain if performed within the first two to three days of symptoms.
Capture ICD-10 Codes Post-Whipple : Reader Questions
Question: A patient developed hypoinsulinemia and diabetes after our surgeon performed a Whipple procedure involving a total pancreatectomy to treat pancreatic cancer in the head of the pancreas. Our surgeon is providing surgical aftercare, while, simultaneously, an oncologist is planning chemotherapy and radiation. What diagnosis codes should we use for […]

Piles Types, Causes and Symptoms | Piles Laser Treatment in Hyderabad
Piles And Laser Surgery What Are Piles? Piles or hemorrhoids are the swollen and dilated blood vessels in the lower rectum and around the anus. In India, eve…
Hemorrhoidectomy | PDF | Hemorrhoid | Surgery
Hemorrhoidectomy – Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Follow Documentation Details for Correct Cystotomy Code : Reader Question
Question: The urologist completed an intraoperative consult and then performed a cystotomy during the patient’s Cesarean section. What cystotomy code should we report? Nebraska Subscriber Answer: You have several cystotomy code choices, depending on your physician’s documentation. The options are:


