Hemorrhoid Surgery – Dallas, TX: Dina Madni, MD
Trusted General Surgeons serving Dallas, TX. Contact us at 972-694-3673 or visit us at 7777 Forest Lane, Suite A-331, Dallas, TX 75230: Dina Madni, MD

Treating hemorrhoidal disease: Conservative vs. surgical approaches | Digestive | UT Southwestern Medical Center Appointment Appointment Appointment Appointment Call Appointment Share via Facebook Share via Twitter Share via LinkedIn Share via Email Print this page Facebook Twitter YouTube
Hemorrhoidal disease affects about 10 million people per year in the U.S., but many people arent aware of the many effective treatment options that are available.
Hemorrhoids: Background, Anatomy, Etiology and Pathophysiology
Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the lower rectum. They are among the most common causes of anal pathology, and subsequently are blamed for virtually any anorectal complaint by patients and medical professionals alike.
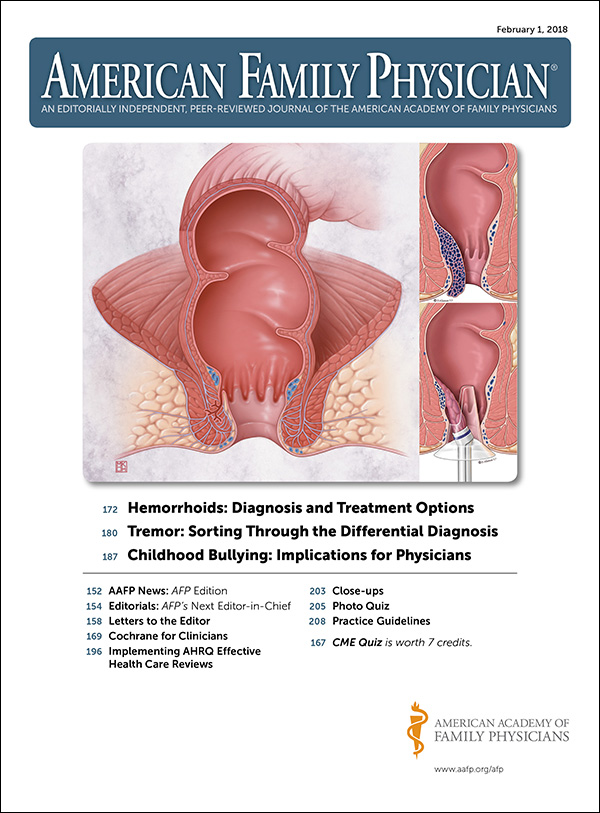
Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis and Treatment Options | AAFP
Many Americans between 45 and 65 years of age experience hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidal size, thrombosis, and location (i.e., proximal or distal to the dentate line) determine the extent of pain or discomfort. The history and physical examination must assess for risk factors and clinical signs indicating more concerning disease processes. Internal hemorrhoids are traditionally graded from I to IV based on the extent of prolapse. Other factors such as degree of discomfort, bleeding, comorbidities, and patient preference should help determine the order in which treatments are pursued. Medical management (e.g., stool softeners, topical over-the-counter preparations, topical nitroglycerine), dietary modifications (e.g., increased fiber and water intake), and behavioral therapies (sitz baths) are the mainstays of initial therapy. If these are unsuccessful, office-based treatment of grades I to III internal hemorrhoids with rubber band ligation is the preferred next step because it has a lower failure rate than infrared photocoagulation. Open or closed (conventional) excisional hemorrhoidectomy leads to greater surgical success rates but also incurs more pain and a prolonged recovery than office-based procedures; therefore, hemorrhoidectomy should be reserved for recurrent or higher-grade disease. Closed hemorrhoidectomy with diathermic or ultrasonic cutting devices may decrease bleeding and pain. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy elevates grade III or IV hemorrhoids to their normal anatomic position by removing a band of proximal mucosal tissue; however, this procedure has several potential postoperative complications. Hemorrhoidal artery ligation may be useful in grade II or III hemorrhoids because patients may experience less pain and recover more quickly. Excision of thrombosed external hemorrhoids can greatly reduce pain if performed within the first two to three days of symptoms.

Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis and Treatment Options | AAFP
Many Americans between 45 and 65 years of age experience hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidal size, thrombosis, and location (i.e., proximal or distal to the dentate line) determine the extent of pain or discomfort. The history and physical examination must assess for risk factors and clinical signs indicating more concerning disease processes. Internal hemorrhoids are traditionally graded from I to IV based on the extent of prolapse. Other factors such as degree of discomfort, bleeding, comorbidities, and patient preference should help determine the order in which treatments are pursued. Medical management (e.g., stool softeners, topical over-the-counter preparations, topical nitroglycerine), dietary modifications (e.g., increased fiber and water intake), and behavioral therapies (sitz baths) are the mainstays of initial therapy. If these are unsuccessful, office-based treatment of grades I to III internal hemorrhoids with rubber band ligation is the preferred next step because it has a lower failure rate than infrared photocoagulation. Open or closed (conventional) excisional hemorrhoidectomy leads to greater surgical success rates but also incurs more pain and a prolonged recovery than office-based procedures; therefore, hemorrhoidectomy should be reserved for recurrent or higher-grade disease. Closed hemorrhoidectomy with diathermic or ultrasonic cutting devices may decrease bleeding and pain. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy elevates grade III or IV hemorrhoids to their normal anatomic position by removing a band of proximal mucosal tissue; however, this procedure has several potential postoperative complications. Hemorrhoidal artery ligation may be useful in grade II or III hemorrhoids because patients may experience less pain and recover more quickly. Excision of thrombosed external hemorrhoids can greatly reduce pain if performed within the first two to three days of symptoms.

Hemorrhoids | SpringerLink
Hemorrhoids are one of the most frequent anorectal disorders encountered in the office setting and are responsible for considerable patient suffering and disability. Hemorrhoids that become symptomatic are initially treated conservatively with dietary changes and…

6 self-help tips for hemorrhoid flare-ups – Harvard Health
Hơn 1.900 Anu hình minh họa, đồ họa vectơ trả phí bản quyền một lần & Clip Art – iStock Bảng
Lựa chọn từ hình minh họa sẵn có Anu trên iStock. Tìm hình ảnh vector trả phí bản quyền một lần chất lượng cao mà bạn sẽ không tìm thấy ở bất kỳ nơi nào khác.

Hemorrhoids | SpringerLink
Proper diagnosis and management of hemorrhoidal disease are essential to ensuring good patient outcomes. Knowledge of anorectal anatomy is critical to select an appropriate treatment strategy. Treatment usually starts with simple lifestyle modifications including…

ANORECTAL DISORDERS – GASTROINTESTINAL EMERGENCIES – Tintinallis Emergency Medicine – Just the Facts, 3ed.
ANORECTAL DISORDERS – GASTROINTESTINAL EMERGENCIES – Tintinallis Emergency Medicine – Just the Facts, 3ed. – by David M. Cline
Colorectal Surgery – Hemorrhoidectomy

Help For Hemorrhoids | Gastro Associates
Left untreated, hemorrhoids often get worse over time and, therefore, are harder to treat, possibly requiring surgery.

Symptomatic Hemorrhoid Treatment – Gastro SB
Hemorrhoids are a common disorder and not usually a serious condition. Learn about remedies for relief and treatments for hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids | Sparrow
OverviewHemorrhoids (HEM-uh-roids), also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower rectum, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids can develop inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids). Nearly three out of four adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes, but often the cause is unknown.
![]()
Hemorrhoidectomy Article
A publicly available article also appearing in PubMed about Hemorrhoidectomy

Surgical anatomy anal canal
Surgical anatomy- anal canal by: Dr. Belal Mansoor Taiz university 18/3/2018 Overview Introductions Location , extent , Dimensions of anal canal Embryology…

Anorectal Disorders – Northwest Surgical Specialists
Hemorrhoids | Sparrow
OverviewHemorrhoids (HEM-uh-roids), also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower rectum, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids can develop inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids). Nearly three out of four adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes, but often the cause is unknown.
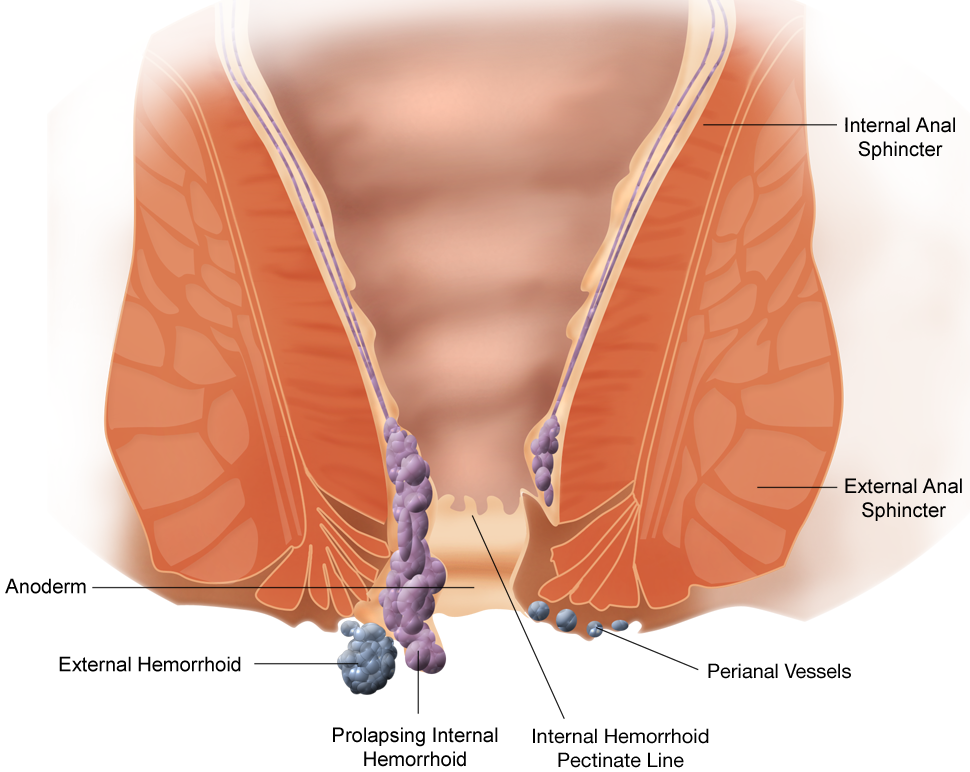
Pectinate line – Wikipedia

Explainer: why do people get haemorrhoids and how do you get rid of them?
Haemorrhoids can be painful, and may sometimes require surgery. We don’t know exactly why they can become problematic but there are some things you can do to reduce the risk of getting them.

Hemorrhoids | SpringerLink
Hemorrhoids are one of the most frequent anorectal disorders encountered in the office setting and are responsible for considerable patient suffering and disability. Hemorrhoids that become symptomatic are initially treated conservatively with dietary changes and…
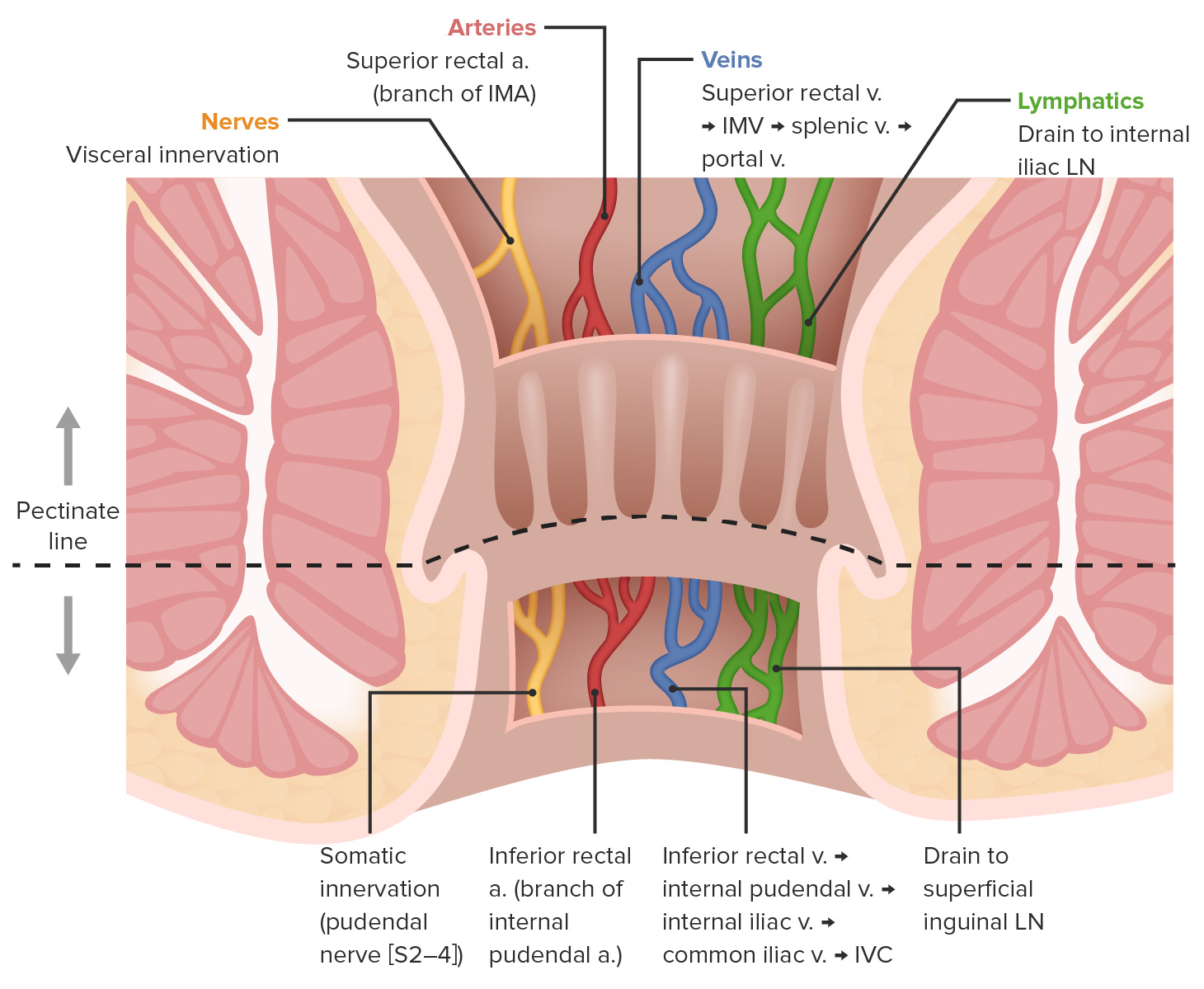
Rectum and Anal Canal: Anatomy | Concise Medical Knowledge
The rectum and anal canal are the most terminal parts of the lower GI tract/large intestine.

Hemorrhoids | Abdominal Key
Hemorrhoids Marvin L. Corman And the men that died not were smitten with the emerods; and the cry of the city went up to heaven. —1 Samuel 5:12* *It is always stimulating to receive comments from readers of prior editions, especially those that are not merely flattering but from which I may learn of mistakes…

Hemorrhoid Treatment Specialist NYC | New York City Hemorrhoid Doctor
Our board-certified gastroenterologists are experts in non-surgical hemorrhoid treatments offering safe and effective same-day removal in Midtown & Upper East Side NYC.

Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis and Treatment Options | AAFP
Many Americans between 45 and 65 years of age experience hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidal size, thrombosis, and location (i.e., proximal or distal to the dentate line) determine the extent of pain or discomfort. The history and physical examination must assess for risk factors and clinical signs indicating more concerning disease processes. Internal hemorrhoids are traditionally graded from I to IV based on the extent of prolapse. Other factors such as degree of discomfort, bleeding, comorbidities, and patient preference should help determine the order in which treatments are pursued. Medical management (e.g., stool softeners, topical over-the-counter preparations, topical nitroglycerine), dietary modifications (e.g., increased fiber and water intake), and behavioral therapies (sitz baths) are the mainstays of initial therapy. If these are unsuccessful, office-based treatment of grades I to III internal hemorrhoids with rubber band ligation is the preferred next step because it has a lower failure rate than infrared photocoagulation. Open or closed (conventional) excisional hemorrhoidectomy leads to greater surgical success rates but also incurs more pain and a prolonged recovery than office-based procedures; therefore, hemorrhoidectomy should be reserved for recurrent or higher-grade disease. Closed hemorrhoidectomy with diathermic or ultrasonic cutting devices may decrease bleeding and pain. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy elevates grade III or IV hemorrhoids to their normal anatomic position by removing a band of proximal mucosal tissue; however, this procedure has several potential postoperative complications. Hemorrhoidal artery ligation may be useful in grade II or III hemorrhoids because patients may experience less pain and recover more quickly. Excision of thrombosed external hemorrhoids can greatly reduce pain if performed within the first two to three days of symptoms.
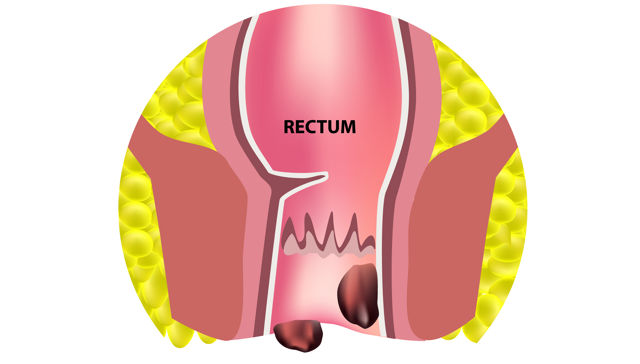
Hemorrhoidectomy
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove hemorrhoids, which are swollen and inflamed veins in the lower rectum and anus. The procedure involves removing the affected tissue, either through traditional surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as laser surgery.

Stock Colon – Rectum: Hemorrhoids — Illustrated Verdict
Colon – Rectum: Hemorrhoids – Medical Legal Illustrations

Hemorrhoids
HEMORRHOIDS Presented by: S.MUTHUKUMARAN 6th year 3rd Group Yerevan Haybusak University SYNOPSIS • Definition • Anatomy and pathophysiology • Etiology • Types…
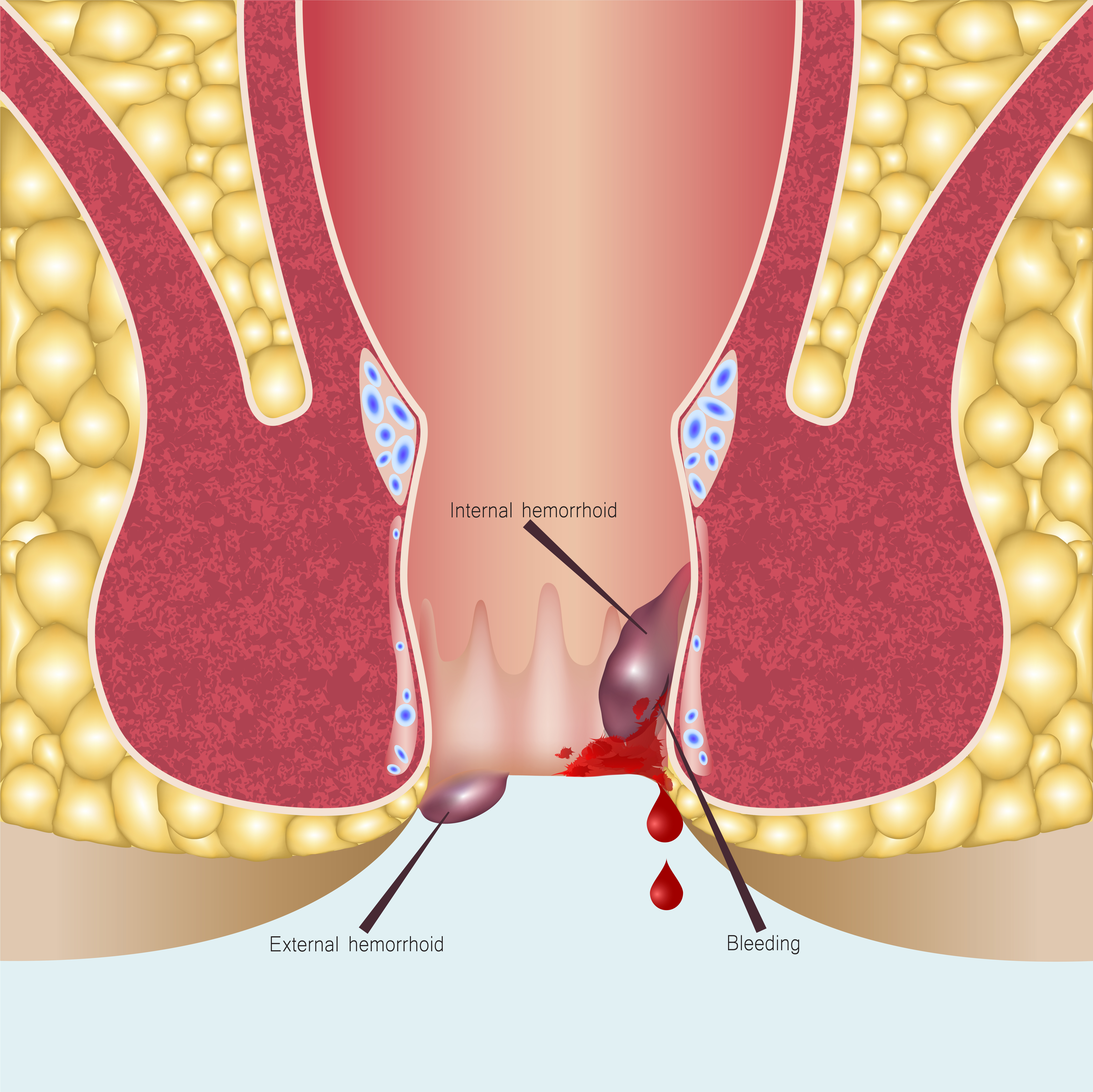
Haemorrhoids: Everyone has them, but they can become problematic | Pharmacy Today
YOU FIND PAUL over by the laxatives, and he asks you what you would recommend for piles, which he says have been bothering him for the past four months, since he started a new job that involves heavy lifting

Hemorrhoid Symptoms Raleigh | Hemorrhoid Treatments
UNC Health Care offers information about the symptoms and treatments of Hemorrhoids for clients in Raleigh, Durham, Wilmington.

Hemorrhoids with Dr. Jasbir Makker | PE GI Solutions
Dr. Makker is a distinguished clinician at Bronx Care Health system, we discuss hemorrhoids and treatment to break the stigma.
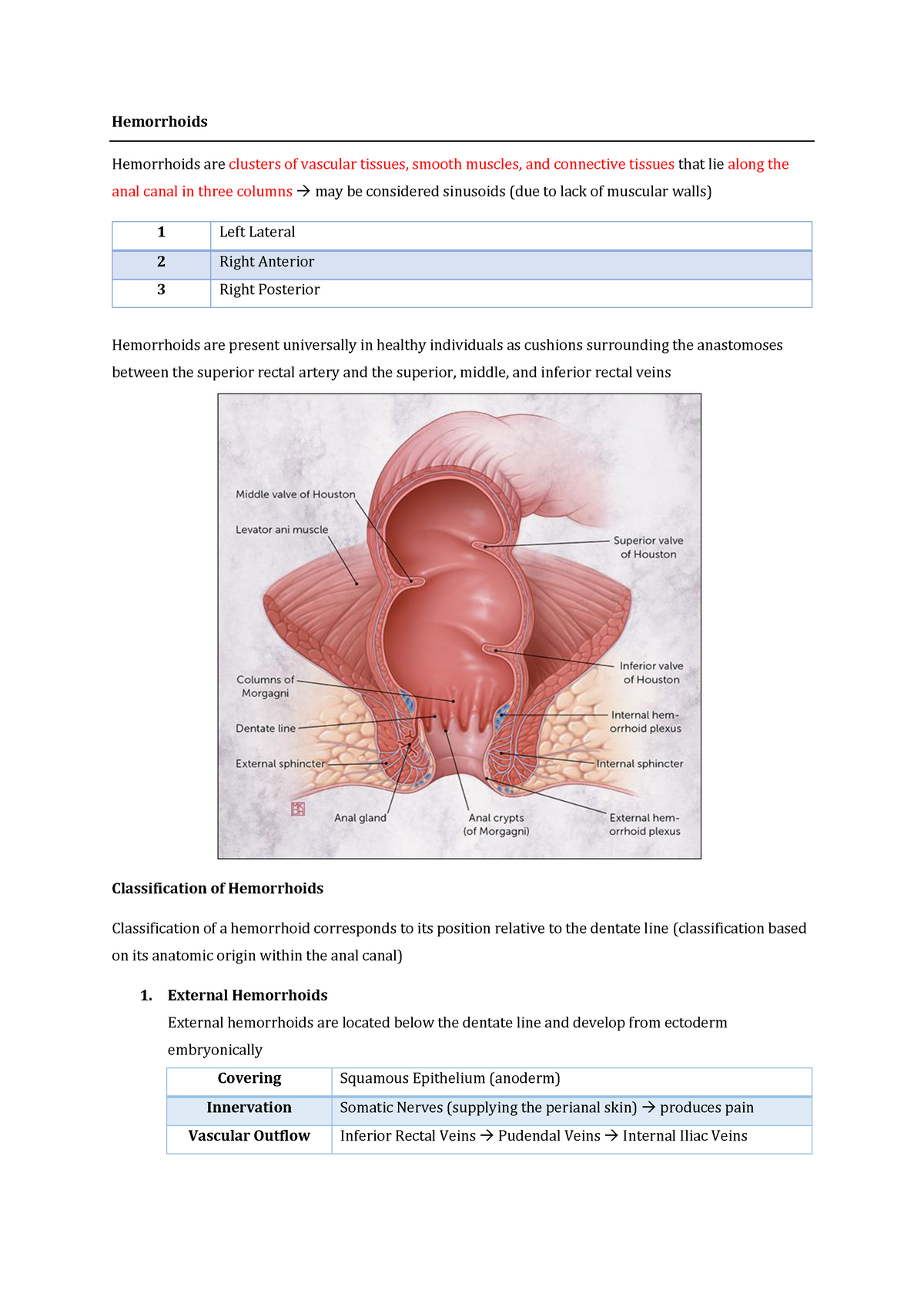
Hemmorhoid – Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are clusters of vascular tissues, smooth muscles, and – Studocu
Hemmorhoid grading, choice of treatment based on grade and approach with different type of hemmorhoid hemorrhoids hemorrhoids are clusters of vascular tissues,
Colorectal Surgery – Hemorrhoidectomy
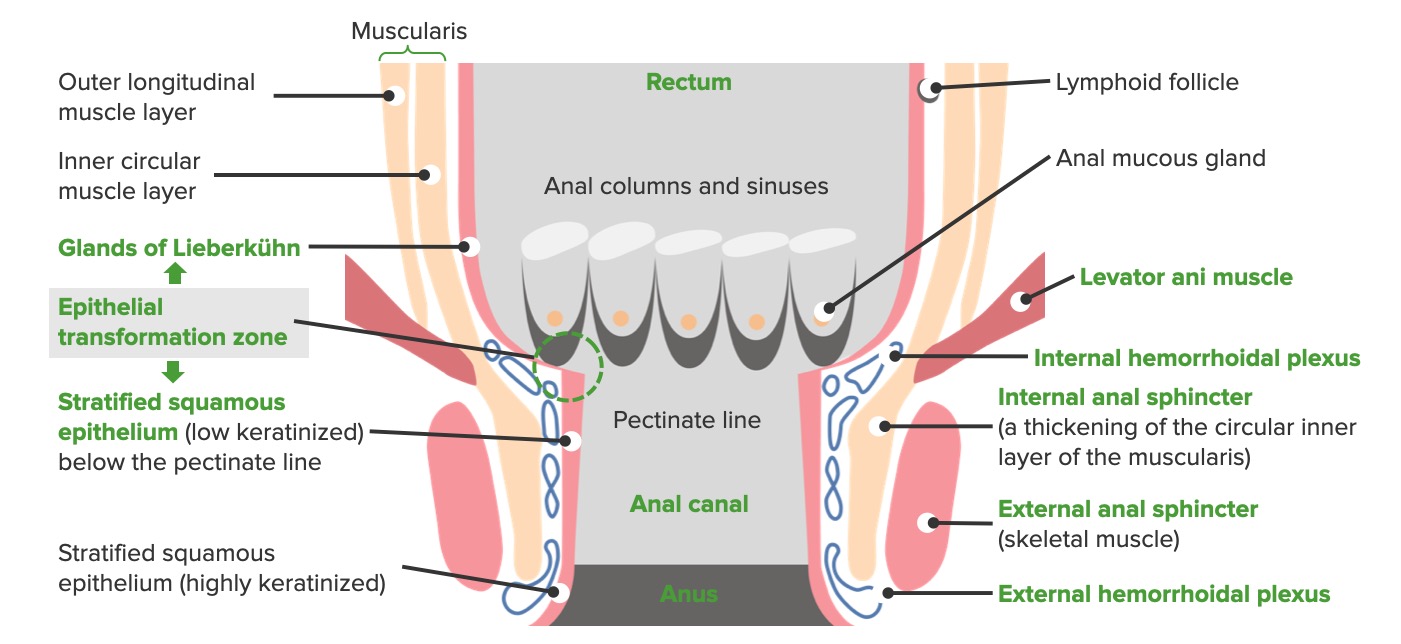
Hemorrhoids | Concise Medical Knowledge
Hemorrhoids are normal vascular cushions in the anal canal, composed of dilated vascular tissue, smooth muscle, and connective tissue.

Hemorrhoid Banding Services Greenville | Gastro Associates
Hemorrhoids can get progressively worse over time. Get relief with our painless & proven hemorrhoid banding services.

HEMORRHOID BANDING | AMD CLINIC | Johor Bahru
Hemorrhoid banding is a non-invasive technique to remove hemorrhoids. It can be performed as a out-patient procedure. It is simple and easy!

Hemorrhoids | SpringerLink
Proper diagnosis and management of hemorrhoidal disease are essential to ensuring good patient outcomes. Knowledge of anorectal anatomy is critical to select an appropriate treatment strategy. Treatment usually starts with simple lifestyle modifications including…
